The primary aim of the policy is to accelerate the exploration activity of minerals in the country through enhanced participation of the private sector.
Why is such a policy needed?
To uncover the full mineral potential of the country and thus put the country’s mineral resources to best use.
National Mineral Exploration policy has the following main features.
- Auctioning of identified exploration block to the private sector on a revenue share basis. That means provision for attracting private investment in exploration through an attractive revenue-sharing model.
- Suppose the explorer agencies do not discover any auction-able resource. In that case, their exploration expenditure will be reimbursed on a normative cost basis. (it means if the explorer agencies do not find any valuable resources during their exploration, they will get their money back based on standard expected costs, which means they will not lose money if they do not find anything worth selling).
- The government will carry out a National Aerogeophysical Program to acquire state-of-the-art baseline data for targeting concealed deposits. ( it means the government will conduct a program by using advanced technology to fetch important baseline data. that will help in identifying hidden deposits which are beneath the Earth’s surface more effectively. The objective is to locate these valuable resources for future exploration and development purposes.
- A National Geoscientific Data Repository is proposed to be set up to collect baseline and mineral exploration information generated by various central and state government agencies and also mineral concession holders and to maintain this geospatial database.
- National Central for Mineral Targeting: it is proposed to be set up as a not-for-profit autonomous institution to address the mineral exploration challenges of the country.
- A special initiative to probe deep/seated concealed minerals( means focused effort or project )
Challenges/Concerns Faced by Mineral Exploration in India:
Displacement and rehabilitation issues:
- Large-scale displacement of local people leads to grievances and improper rehabilitation measures, thereby, leading to people’s alienation and develop distrust over the government machinery.
- It’s not just a loss of land for the local population but rather the loss of a tribal way of life and their rich cultural heritage.
- It has given space to left-wing extremism in resource-rich areas like Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, etc.
- Mining also puts the lives of miners at risk due to the rudimentary ways adopted and the absence of adequate safety gear and protocols. For instance, mine-related accidents at the Ksan coal mine in Meghalaya- Jaintia Hills (2018), Chasnala near Dhanbad in 1975.
- Human Rights violations have taken place in the form of mine-related deaths, inadequate rehabilitation, developmental steps, etc. Massive local protests have taken place against mining in Niyamgiri Hills of Odisha, POSCO in Odisha, Sterlite protest in T.N.
- Rathole mining: This is a form of illegal mining, especially practised in Northeastern areas like Meghalaya (Ksan coal mine incident). It involves digging very small tunnels [only 3-4 feet high], done both vertically and horizontally. The NGT banned it in 2015 on the grounds of it being unscientific and unsafe for workers.
- The coal seam is extremely thin in Meghalaya, no other methods would not be economically viable. Removal of rocks from the hilly terrain and putting up pillars inside the mine to prevent collapse would be costlier. In Meghalaya, this is the locally developed technique and the most commonly used one.
Environmental/Health issues
- Environmental pollution has been caused by the Makrana marble mines in Rajasthan, the Granite mines of Karnataka have left a large hole in the earth, Damodar River has been severely polluted by coal mining.
- Loss of biodiversity and local heritage due to mining activities.
- The prevalence of mining in an area causes various diseases like fibrosis, Pneumoconiosis, and silicosis in workers as well as locals.
- Water Pollution – water from streams and rivers in mining areas has become acidic and unfit for drinking. Eg: Meghalaya’s Kopili river, Damodar river etc.
- Contaminated air with high particulate matter is also a major problem in mining-rich regions.
Administrative issues
- Arbitrary allocation of coal mines leads to long litigation and eventually cancellation of allocations and charges of corruption in block allocations.
- Delay in environmental clearances due to bureaucratic hindrances.
- Judicial interventions lead to long delays and losses for investors. For example, SC imposed a heavy penalty on illegal mining without green clearances in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, and Odisha in 2017. Banning of Vedanta group in Niyamgiri Hills of Odisha and shut down of 88 illegal mining leases in Goa in 2018.
B) National Geoscience Data Repository ( Dec 2023)
Recently Union Minister Prahlad Joshi launched National Geoscience Data Repository Portal ( NGDRP) in December 2023
Ministry of Mines:
NGDR has been created, as a part of the NMEP 2016, hosting all baseline and exploration related geoscientific data in a single GIS platform, to expedite, enhance and facilitate the exploration coverage of the country.
- The survey is spearheaded by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and the Bhaskaracharya Institute of Space Application and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N).
- » It will make available all geological, geochemical, geophysical, and mineral exploration data in the public domain on a digital geospatial platform. This will include baseline geoscience data and all mineral exploration information generated by various central and state government agencies and mineral concession holders.
- » It represents a significant leap forward in democratizing critical geoscience data, empowering stakeholders across industries and academia with unprecedented access to valuable resources.
- https://geodataindia.gov.in.
c) OFFSHORE AREAS MINERAL ( DEVELOPMENT AND REGULATION) AMMENDMWHYENT ACT 2023 ( National Act)
Why in news?
Recently the act was introduced in Loksabha (July 27, 2023), passed in Loksabha ( Aug 01, 2023), and passed in Rajsabha as well (Aug 03, 2023).
- About the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act 2002 (OAMDRA, 2022) » The act regulates mining in maritime zones of India.
» It categorizes offshore mining-related activities into:
▫ (i) Reconnaissance, which involves a preliminary survey to locate mineral resources.
▫ (ii)Exploration, which includes exploring, proving, or locating mineral deposits, and
▫ (iii) Production, the commercial activity of the extraction of minerals.
» The act came into force in 2010.
» However, no mining activity has been undertaken in the offshore areas to date. Therefore, the central government has brought some changes which are focused on improving the ease of doing business.
- Key Highlights of the amendment:
» Introduction of Composite License:
▫ The act provides for a reconnaissance permit, exploration license and a production lease.
▫ The amendment introduces a composite license for granting rights for exploration as well as for production. Under the composite license, the licensee will be required to complete exploration within three years. - The maximum area of exploration under a composite license will be 30 minutes latitude and 30 minutes longitude. The maximum area for undertaking production under a single composite license will be 15 minutes latitude and 15 minutes longitude.
- Extension in the validity of concession:
» The act provides that a concession lease be granted for 30 years and can be further renewed for up to 20 years.
» The amendment provides that the production lease, as well as the production lease under a composite license, will be valid for 50 years. - Competitive bidding for production lease and composite lease:
» The act provides for the grant of concession through administrative allocation.
» The amendment, mandates competitive bidding, for a production lease and a composite license to private entities. - Government Joint Ventures allowed to mine in reserved areas:
» The act allows the government to reserve offshore areas that are not held under any operating
right.
» The amendment allows the composite license or production license to the government or government company. Joint ventures of government companies will also be eligible, subject to certain conditions. These conditions are: - Partners must be selected through a competitive process.
- Government company owns at least 74% of the paid-up capital.
- Mining of atomic minerals only by the Government:
- » The amendment, says that in the case of atomic minerals, exploration, production and composite licenses will be granted only to the government or government companies.
- » Note: What are atomic minerals?
- They are defined under MMDRA, 1957 and include:
Rare Earth Minerals containing Uranium and Thorium Pitchblende and Uranium Ores Uriniferous allanite, monazite and other thorium ores. - Reduction in Standard Area Blocks:
» The Act, the size of one block for offshore mining is five minutes latitude by five minutes longitude.
» The amendment reduces this to one-minute latitude and one-minute longitude. It also limits the maximum area one entity can acquire under all concessions to 45 minutes latitude by 45 minutes longitude. - Offshore Areas Mineral Trust (OAMT) set up:
» The amendment creates OAMT. The concession holder will be required to pay an amount to the Trust in addition to any royalty.
» The fund can be used for specified purposes including - (i) exploration in offshore areas
- (ii) research and studies about the mitigation of adverse effects of offshore mining on the ecology, an
- (iii) Relief upon the occurrence of a disaster.
- Increase in fines for violating the law.
- Note: Royalty, Auction Premium and other revenues from the production of minerals from offshore
areas shall accrue to the Government of India.
Things you should remember for Exam in Above article:
Objective of NMEP:
Search minerals in Country by involving private companies.
Key features:
- Auction Exploration Blocks: This means Private companies can explore minerals in specific areas and share their profits with the government.
- Cost Reimbursement: If companies spend money on exploration but find nothing valuable, the government will pay them back.
- NAP: the government will use advanced technology to find hidden minerals underground.
- Geoscientific Data Repository: A large database that collects all information about mineral exploration.
- NCMT: A special organization to help solve problems in finding minerals.
- Special Initiative for Deep-Seated Minerals: A focused effort would be made to reach to minerals.
Challenges In Mineral Exploration in IHZndia:
- Social impact: people losing their habitat due to mining, leading to chaos, conflict, protest and mistrust in the government.
- Local culture and way of living will be affected by mining activities.
- Safety Concern: Miners face risks such as accidents and health problems due to unsafe conditions.
- Environmental Impact: Mining causes pollution, harms local wildlife, and contaminates water and air. People who live near mines suffer from health issues.
- Administrative issues: Delays in getting permissions and legal disputes making mining difficult.
National Geoscience Data Repository( NGDR)
Purpose:
It stores all important geological and exploration data in one place for easier access.
Managed By:
Geological Survey of India (GSI) and Bhaskaracharya institute of space Application and GeoiNFORMATICS (BISAG-N).
Offshore Areas Mineral ( Development and Regulation) Act 2023:
Objective:
Regulate mining in ocean areas to make it easier for businesses.
Key changes:
New licenses for both exploring and mining minerals.
Bidding system for companies to get mining rights.
special rules for mining certain minerals and involving the government in joint ventures.
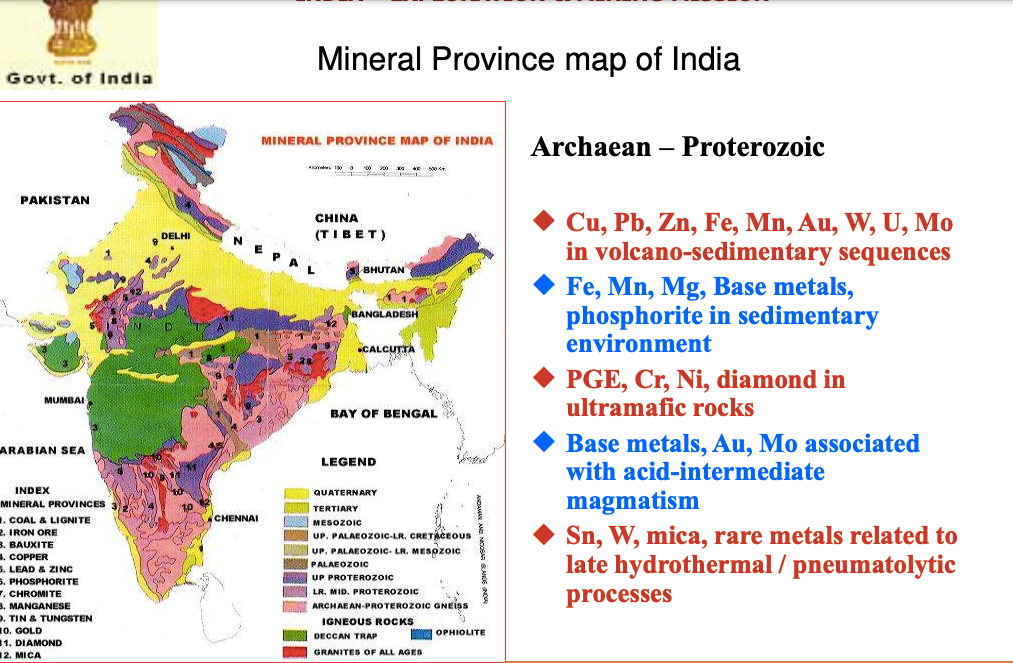
Mineral Resources in India:
Practice this question :
Discuss the objectives of the National Mineral Exploration Policy (NMEP) and explain how private sector participation and technological advancements are expected to address challenges in mineral exploration in India. Highlight potential socio-economic and environmental impacts. (250 words).
Ans) Mindmap
Objectives of NMEP:
- Accelerate mineral exploration
- Enhance private sector participation
- Utilize advanced technology Private Sector Participation
- Auction of exploration blocks
- Revenue-sharing model
- Encourage investments in Technological Advancements
| - National Aerogeophysical Program
- Geoscientific Data Repository
- National Center for Mineral Targeting Addressing Challenges
- Displacement and rehabilitation issues
- Safety concerns for miners
- Environmental impacts (pollution, biodiversity loss) Socio-economic Impacts
- Economic benefits (job creation, revenue generation)
- Social issues (displacement, protests) Environmental Impacts
- Pollution (water, air)
- Biodiversity loss
- Health risks for communities Conclusion
- Overall impact assessment
- The balance between development and conservation
example :
The National Mineral Exploration Policy (NMEP) aims to speed up mineral exploration in India by involving private companies and using advanced technology. The policy focuses on auctioning exploration blocks to attract private investment and sharing revenue from mineral discoveries. It also promotes initiatives like the National Aerogeophysical Program and Geoscientific Data Repository to enhance exploration efficiency.
Private sector participation is crucial for funding and conducting explorations. Technological advancements, such as aero geophysical surveys and centralized data repositories, help target mineral deposits more effectively.
These efforts address challenges like displacement, safety risks for miners, and environmental impacts such as pollution and biodiversity loss. While mineral exploration brings economic benefits like job creation and revenue, it also raises social and environmental concerns.
To mitigate adverse impacts, a balanced approach is needed, ensuring sustainable practices and community engagement. Overall, the NMEP emphasizes leveraging private expertise and technology to maximize mineral resource utilization while minimizing negative socio-economic and environmental effects.
| To know more about Mineral resources visit: https://teachmint.storage.googleapis.com/public/235675593/StudyMaterial/35c9fe3a-f1aa-4c4b-9b4d-368261034eae.pdf |
| To read Man and Biosphere Reserve click: https://mateenahaya.com/biosphere-reserve/,/https://mateenahaya.com/mankind-have-always-wandered-or-settled-agreed-or-quarrelled-in-troops-and-companies-adam-ferguson-1723-1816/ To be updated click: Instagram / Facebook |
just remember the main points and try to write again and again, make flashcards to remember for UPSC exam
Try these questions as well
- What is the primary aim /objective of the National Mineral Exploration Policy (NMEP) in India?
a) To limit mineral exploration activities
b) to accelerate mineral exploration with enhanced private -sector participation
c) To restrict Private sector involvement in mineral exploration
d) to reduce technological advancements in exploration.
2. Which of the following is not key feature of the National Mineral Exploration Policy (NMEP)?
A) Reimbursement of exploration costs
B) National Aerogeophysical Program
C) Encouraging displacement of local communities
D) Geoscientific Data Repository
Correct Answer: C
- What does the National Aerogeophysical Program aim to achieve?
A) Enhance private sector participation in mineral exploration
B) Provide subsidies to exploration agencies
C) Acquire baseline data for targeting concealed mineral deposits
D) Encourage protests against mining activities
Correct Answer: C
- What is the significance of private sector participation in mineral exploration according to the article?
A) It limits technological advancements
B) It leads to displacement of local communities
C) It attracts investments and expertise
D) It causes environmental pollution
Correct Answer: C
- Which initiative aims to create a centralized database for mineral exploration information?
A) National Center for Mineral Targeting
B) National Aerogeophysical Program
C) Geoscientific Data Repository
D) Special Initiative for Deep-Seated Minerals.
HOW TO SOLVE THIS TYPE OF QUESTION IN PRELIMS AND MAINS BELOW IS THE TIPS:
Tips for Prelims
- Focus on understanding the objective, features, and key features of the NMEP and related programmes such as NAP and GDR.
- study specific details example keep yourself continuously updated on technological advancement, and private sector participation and their role in addressing challenges like displacement, safety concerns and environmental impacts.
- Practice multiple-choice questions.
- Use keywords
- Refer to current affairs.
Tips for mains
- Structure Your answer example starts with defining the objectives
- Concisely explain key features.
- Explain with examples.
- Discuss impact and Implications.
- Include case studies such as impact on local communities, or successful implementation of exploration programs to enrich your answer and provide concrete evidence.
- Provide a balanced perspective: Conclude your answer by emphasizing the importance of balancing both developments as well as environmental conservation.
- Use clear simple language and structure.
By following above tips , you can effectively approach and answer the question related such as type of topics and do not forget to revise current affairs before exam.
Pingback: Top 5 indian infrastructure project ( Best for upsc 2024)